CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes : Thermodynamics
7 Mar 2017
The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa.
A
thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
macroscopic variables (like pressure, volume, temperature, mass,
composition etc) that characterise the system do not change with time.
Thermodynamical System
An
assembly of an extremely large number of particles whose state can be
expressed in terms of pressure, volume and temperature, is
called thermodynamic system.
Thermodynamic system is classified into the following three systems
(i) Open System It exchange both energy and matter with surrounding.
(ii) Closed System It exchanges only energy (not matter) with surroundings.
(iii) Isolated System It exchanges neither energy nor matter with the surrounding.
A
thermodynamic system is not always in equilibrium. For example, a gas
allowed to expand freely against vacuum. Similary, a mixture of petrol
vapour and air, when ignited by a spark is not an equilibrium state.
Equilibrium is acquired eventually with time.
Thermodynamic Parameters or Coordinates or Variables
The
state of thermodynamic system can be described by specifying pressure,
volume, temperature, internal energy and number of moles, etc. These are
called thermodynamic parameters or coordinates or variables.
Work done by a thermodynamic system is given by
W = p * ΔV
where p = pressure and ΔV = change in volume.
Work done by a thermodynamic system is equal to the area enclosed between the p-V curve and the volume axis
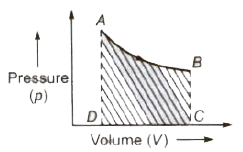
Work done in process A-B = area ABCDA
Work
done by a thermodynamic system depends not only upon the initial and
final states of the system but also depend upon the path followed in the
process.
Work done by the Thermodynamic System is taken as
Positive → 4 as volume increases.
Negative → 4 as volume decreases.
Internal Energy (U)
The total energy possessed by any system due to molecular motion and molecular configuration, is called its internal energy.
Internal energy of a thermodynamic system depends on temperature. It is the characteristic property of the state of the system.
Zeroth Law of ThermodynamicsFirst Law of Thermodynamics
Heat given to a thermodynamic system (ΔQ) is partially utilized in doing work (ΔW) against the surrounding and the remaining part increases the internal energy (ΔU) of the system.
Therefore, ΔQ = ΔU + ΔW
First law of thermodynamics is a restatement of the principle conservation of energy.
In isothermal process, change in internal energy is zero (ΔU = 0).
Therefore, ΔQ = ΔW
In adiabatic process, no exchange of heat takes place, i.e., Δθ = O.
Therefore, ΔU = – ΔW
In adiabatic process, if gas expands, its internal energy and hence, temperature decreases and vice-versa.
In isochoric process, work done is zero, i.e., ΔW = 0, therefore
ΔQ = ΔU
Thermodynamic Processes
A thermodynamical process is said to take place when some changes’ occur in the state of a thermodynamic system i.e., the therrnodynamie parameters of the system change with time.
(i) Isothermal Process A process taking place in a thermodynamic system at constant temperature is called an isothermal process.
Isothermal processes are very slow processes.
These process follows Boyle’s law, according to which
pV = constant
From dU = nCvdT as dT = 0 so dU = 0, i.e., internal energy is constant.
From first law of thermodynamic dQ = dW, i.e., heat given to the system is equal to the work done by system surroundings.
Work done W = 2.3026μRT l0g10(Vf / Vi) = 2.3026μRT l0g10(pi / pf)
where, μ = number of moles, R = ideal gas constant, T = absolute temperature and Vi Vf and Pi, Pf are initial volumes and pressures.
After differentiating P V = constant, we have

i.e., bulk modulus of gas in isothermal process, β = p.
P – V curve for this persons is a rectangular hyperbola
Examples
(a) Melting process is an isothermal change, because temperature of a substance remains constant during melting.
(b) Boiling process is also an isothermal operation.
(ii) Adiabatic Process A process taking place in a thermodynamic system for which there is no exchange of heat between the system and its surroundings.
Adiabatic processes are very fast processes.
These process follows Poisson’s law, according to which
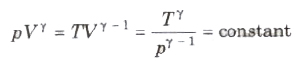
From dQ = nCdT, Cadi = 0 as dQ = 0, i.e., molar heat capacity for adiabatic process is zero.
From first law, dU = – dW, i.e., work done by the system is equal to decrease in internal energy. When a system expands adiabatically, work done is positive and hence internal energy decrease, i.e., the system cools down and vice-versa.
Work done in an adiabatic process is
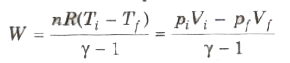
where Ti and Tf are initial and final temperatures. Examples
(a) Sudden compression or expansion of a gas in a container with perfectly non-conducting wall.
(b) Sudden bursting of the tube of a bicycle tyre.
(c) Propagation of sound waves in air and other gases.
(iii) Isobaric Process A process taking place in a thermodynamic system at constant pressure is called an isobaric process.
Molar heat capacity of the process is Cp and dQ = nCpdT.
Internal energy dU = nCv dT
From the first law of thermodynamics
dQ = dU + dW
dW = pdV = nRdT
Process equation is V / T = constant.
p- V curve is a straight line parallel to volume axis.
(iv) Isochoric Process A process taking place in a tlaermodynars system at constant volume is called an isochoric process.
dQ = nCvdT, molar heat capacity for isochoric process is Cv.
Volume is constant, so dW = 0,
Process equation is p / T = constant
p- V curve is a straight line parallel to pressure axis.
(v) Cyclic Process When a thermodynamic system returns to . initial state after passing through several states, then it is called cyclic process.
Efficiency of the cycle is given by
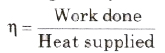
Work done by the cycle can be computed from area enclosed cycle on p- V curve.
Isothermal and Adiabatic Curves
The graph drawn between the pressure p and the volume V of a given mass of a gas for an isothermal process is called isothermal curve and for an adiabatic process it is called adiabatic curve .

The slope of the adiabatic curve
= γ x the slope of the isothermal curve
Volume Elasticities of Gases
There are two types of volume elasticities of gases
(i) Isothermal modulus of elasticity ES = p
(ii) Adiabatic modulus of elasticity ET = γ p
Ratio between isothermal and adiabatic modulus
ES / ET = γ = Cp / CV
where Cp and Cv are specific heats of gas at constant pressure and at constant volume.
For an isothermal process Δt = 0, therefore specific heat,
c = Δ θ / m Δt = &infi;
For an adiabatic process 119= 0, therefore specific heat,
c = 0 / m Δt = 0
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics gives a fundamental limitation to the efficiency of a heat engine and the coefficient of performance of a refrigerator. It says that efficiency of a heat engine can never be unity (or 100%). This implies that heat released to the cold reservoir can never be made zero.
Kelvin’s Statement
It is impossible to obtain a continuous supply of work from a body by cooling it to a temperature below the coldest of its surroundings.
Clausius’ Statement
It is impossible to transfer heat from a lower temperature body to a higher temperature body without use of an extemal agency.
Planck’s Statement
It is impossible to construct a heat engine that will convert heat completely into work.
All these statements are equivalent as one can be obtained from the other.
Entropy
Entropy is a physical quantity that remains constant during a reversible adiabatic change.
Change in entropy is given by dS = δQ / T
Where, δQ = heat supplied to the system
and T = absolute temperature.
Entropy of a system never decreases, i.e., dS ≥ o.
Entropy of a system increases in an irreversible process
Heat Engine
A heat energy engine is a device which converts heat energy into mechanical energy.
A heat engine consists of three parts
(i) Source of heat at higher temperature
(ii) Working substance
(iii) Sink of heat at lower temperature
Thermal efficiency of a heat engine is given by
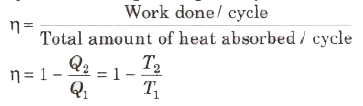
where Q1 is heat absorbed from the source,
Q2 is heat rejected to the sink and T1 and T2 are temperatures of source and sink.
Heat engine are of two types
(i) External Combustion Engine In this engine fuel is burnt a chamber outside the main body of the engine. e.g., steam engine. In practical life thermal efficiency of a steam engine varies from 12% to 16%.
(ii) Internal Combustion Engine In this engine. fuel is burnt inside the main body of the engine. e.g., petrol and diesel engine. In practical life thermal efficiency of a petrol engine is 26% and a diesel engine is 40%.
Carnot’s Cycle
Carnot devised an ideal cycle of operation for a heat engine, called Carnot’s cycle.

A Carnot’s cycle contains the following four processes
(i) Isothermal expansion (AB)
(ii) Adiabatic expansion (BO)
(iii) Isothermal compression (CD)
(iv) Adiabatic compression (DA)
The net work done per cycle by the engine is numerically equal to the area of the loop representing the Carnot’s cycle .
After doing the calculations for different processes we can show that

[Efficiency of Carnot engine is maximum (not 1000/0) for given temperatures T1 and T2. But still Carnot engine is not a practical
engine because many ideal situations have been assumed while designing this engine which can practically not be obtained.]
Refrigerator or Heat Pump
A refrigerator or heat pump is a device used for cooling things. It absorb heat from sink at lower temperature and reject a larger amount of heat to source at higher temperature.
Coefficient of performance of refrigerator is given by

where Q2 is heat absorbed from the sink, Q1 is heat rejected to source and T1 and T2 are temperatures of source and sink.
Relation between efficiency (η) and coefficient of performance (β)

